Interlocking Systems: Enhancing Mold Performance and Product Quality
Hi there! Dan here, back with another deep dive into the world of tooling molds.
In the intricate dance of injection molding, precision is paramount. With each cycle, the seamless alignment of mold components ensures the smooth production of high-quality parts. While guiding pins and bushes are well-known players in this symphony of movement, there's another crucial element often working behind the scenes: interlocks.
These unassuming components may not always take center stage, but their role in facilitating the precise opening and closing of molds is indispensable. Join me as we unravel the mysteries of interlocks and discover the vital role they play in the injection molding process.

A parting line interlock refers to a design feature in a mold where the two halves of the mold (usually the core and cavity halves) are interlocked or aligned precisely along the parting line during mold closure. The parting line is the boundary where these two mold halves meet and separate to allow the molded part to be ejected.
The purpose of a parting line interlock is to ensure that the mold halves close together accurately and remain securely aligned during the molding process. This alignment is crucial for producing high-quality parts with consistent dimensions and surface finish. Parting line interlocks help prevent issues such as flash (excess material along the parting line), mismatched features, or dimensional inaccuracies caused by misalignment of the mold halves.

Parting line interlocks can take various forms depending on the design of the mold. Common types include mechanical interlocks, where mating features on the mold halves physically engage to ensure alignment, and geometric interlocks, where tapered or angled surfaces help guide the mold halves into position during closure. The specific type of interlock used depends on factors such as the complexity of the mold design, the materials being molded, and the requirements of the final parts.
Here's information about 3 types of interlock commonly used in mold design:
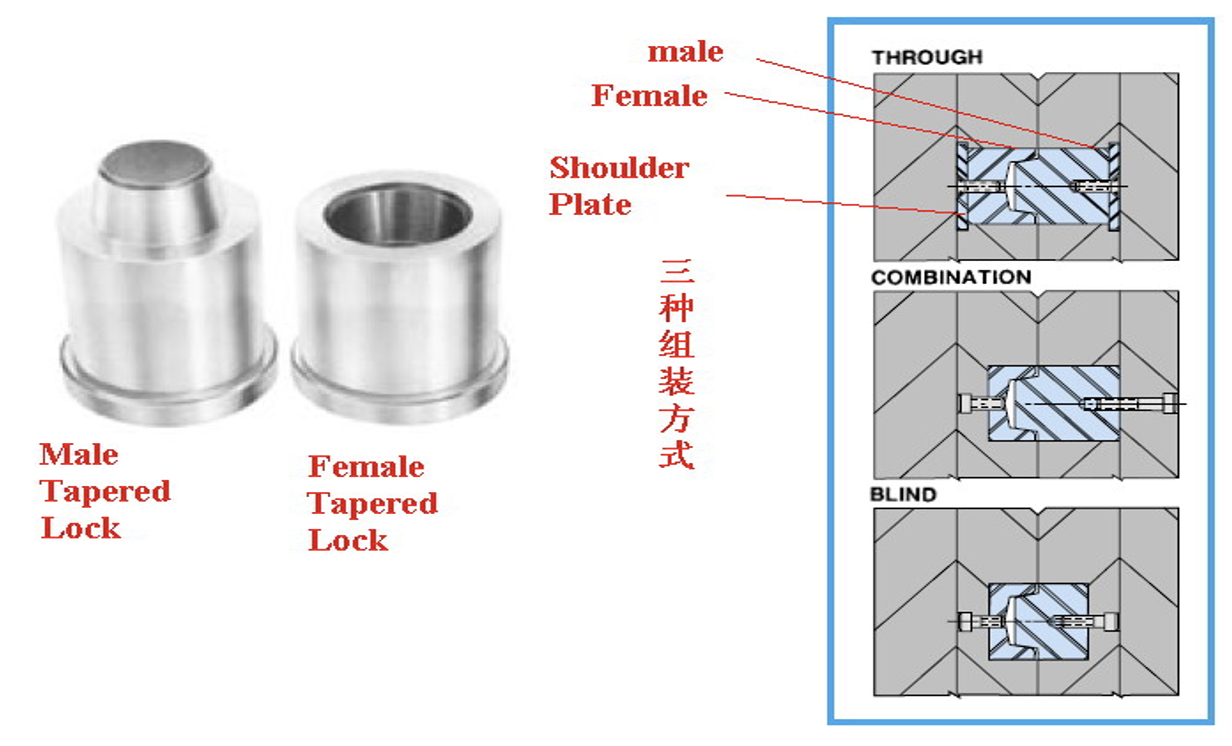
Tapered Interlocks (Round):
- Description: Tapered interlocks are cylindrical features that taper along their length. They are often used in molds to ensure proper alignment and mating of the core and cavity halves during mold closure.
- Function: As the mold closes, the tapered interlocks guide the mold halves into precise alignment along the parting line. This helps prevent flash, ensures consistent part dimensions, and facilitates smooth ejection of the molded parts.
- Advantages: Tapered interlocks provide a self-aligning mechanism that compensates for minor misalignments and wear over time. They also minimize the risk of damage to the mold during operation.
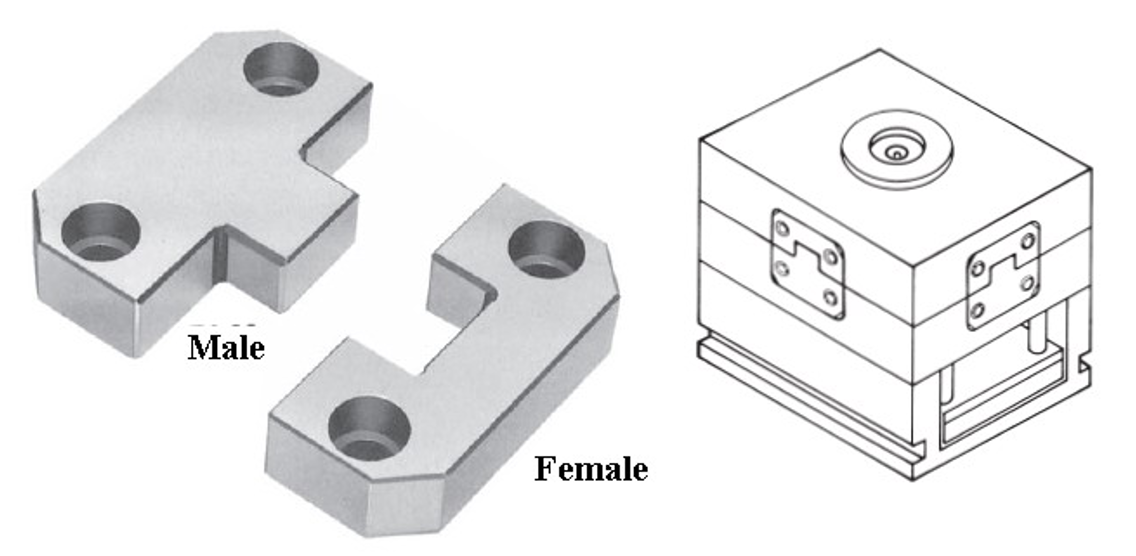
Taper Interlock (Rectangular):
- Description: Taper interlocks, similar to tapered interlocks, are features that have a tapered profile. However, unlike cylindrical tapered interlocks, taper interlocks have a rectangular or trapezoidal cross-section.
- Function: Taper interlocks serve the same purpose as cylindrical tapered interlocks, guiding the mold halves into alignment and preventing misalignment during closure. They are particularly useful for molds with rectangular or square parting lines.
- Advantages: Taper interlocks provide reliable alignment and ensure proper closure of the mold halves, contributing to the production of high-quality parts with consistent dimensions and surface finish.
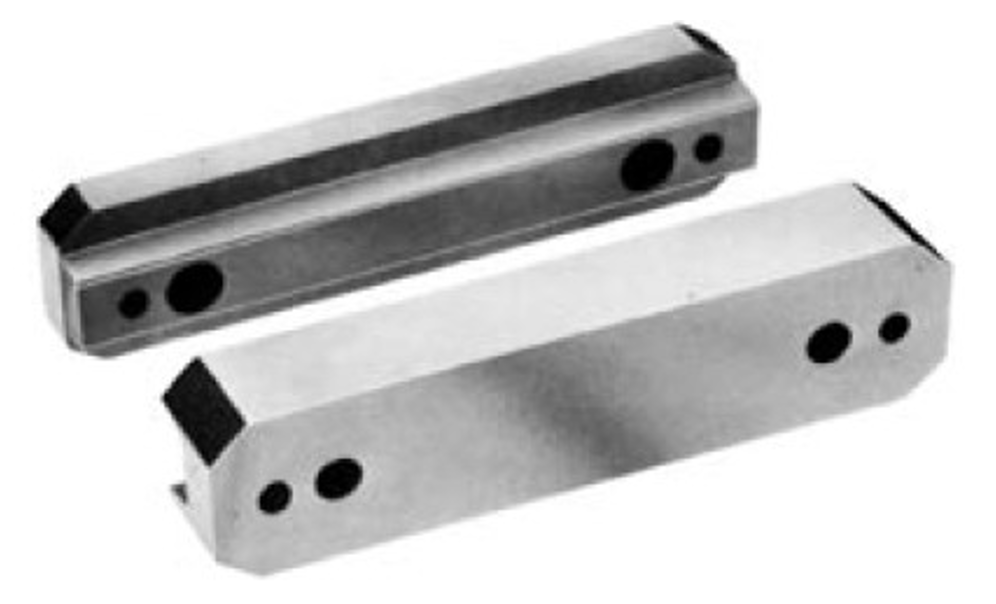


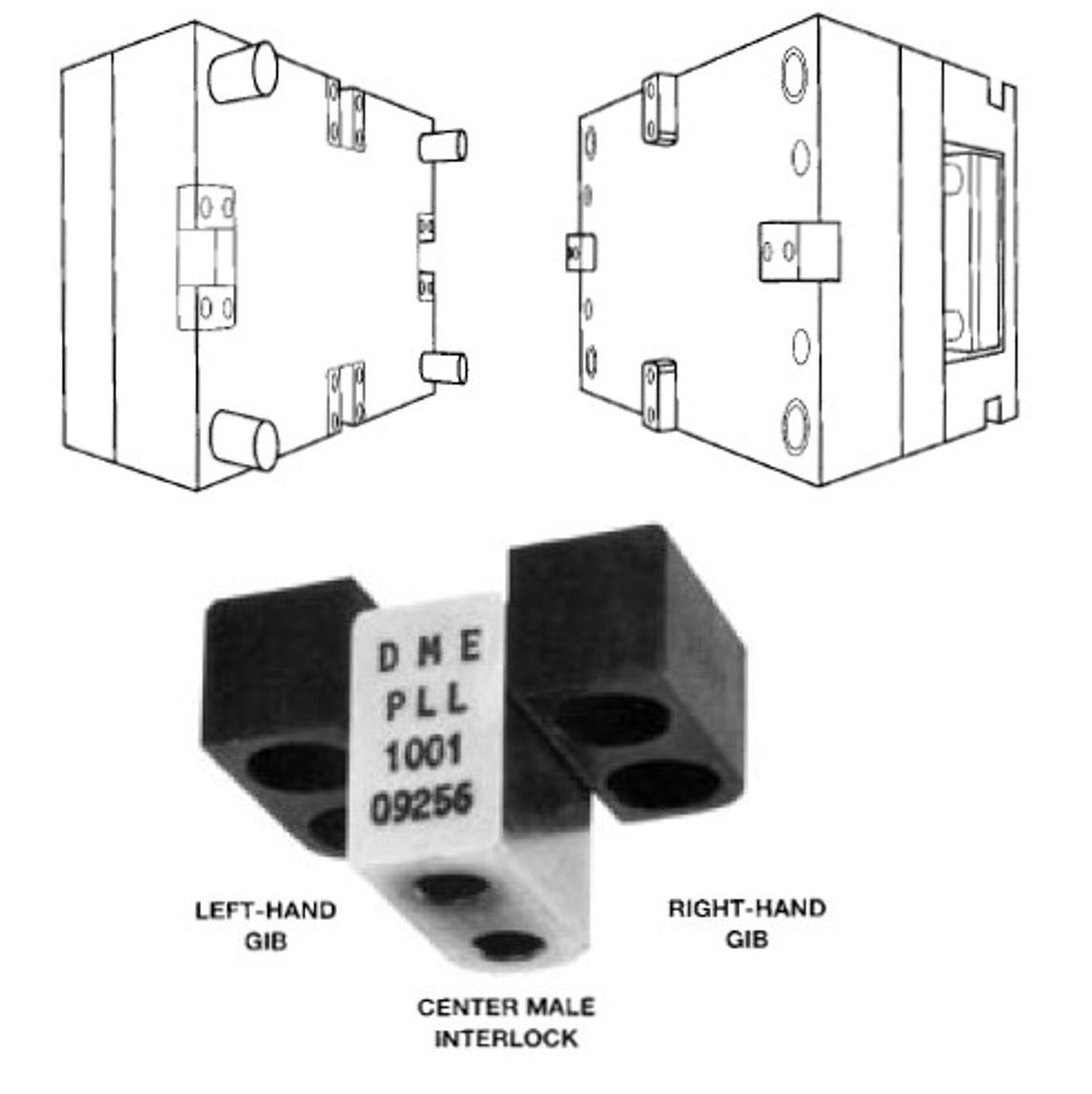
Side Lock (Straight Side Interlock):
- Description: Side locks, also known as straight side interlocks, are mechanical features located along the sides of the mold. They typically consist of matching recesses and protrusions on the core and cavity halves that engage when the mold closes.
- Function: Side locks secure the mold halves together laterally, in addition to the alignment provided by tapered interlocks along the parting line. This prevents lateral movement or shifting of the mold halves during injection and ejection processes.
- Advantages: Side locks enhance the stability of the mold assembly, reducing the risk of flash, parting line defects, and dimensional variations in the molded parts. They are particularly effective for molds with large surface areas or complex geometries.

Each type of interlock plays a crucial role in ensuring the precise alignment, stability, and performance of the mold during the injection molding process. The selection of interlocks depends on factors such as the mold design, material properties, part geometry, and production requirements.
Thanks for your reading!
From parting line locks to tapered interlocks and side locks, each type serves a specific purpose in maintaining alignment and preventing damage during mold closing. By understanding their functions and incorporating them effectively into mold designs, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, minimize downtime, and produce higher quality parts.
So, the next time you marvel at the precision of an injection-molded component, remember the unsung heroes working quietly behind the scenes – the interlocks that play a crucial role in bringing your designs to life.
As always, stay curious, stay innovative, and keep exploring the fascinating world of tooling molds.
Dan
Business development manager
Phone: +86 134 1699 5669
Skype: danny@opro-tech.com Factory add: No 39, Zhen an west road, Changan town , Dong guan city, China.
Injection Mold / CNC Machining / 3D Printing / Prototyping