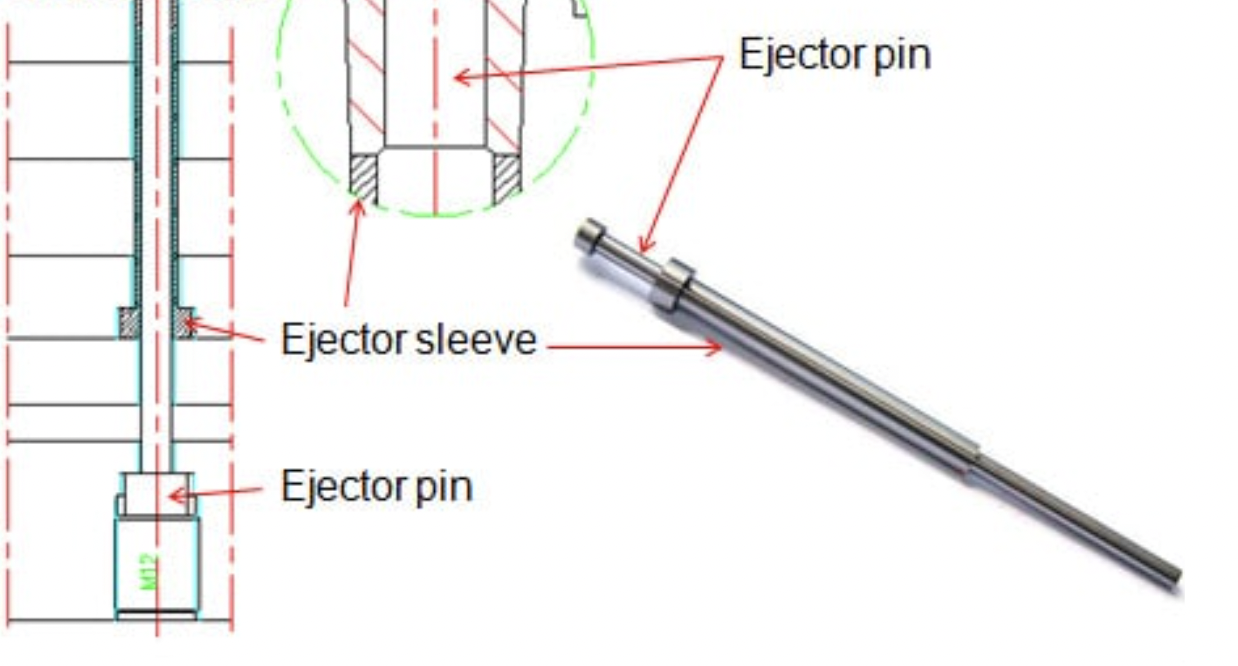
What are ejector pins, core pins and ejector sleeves ?
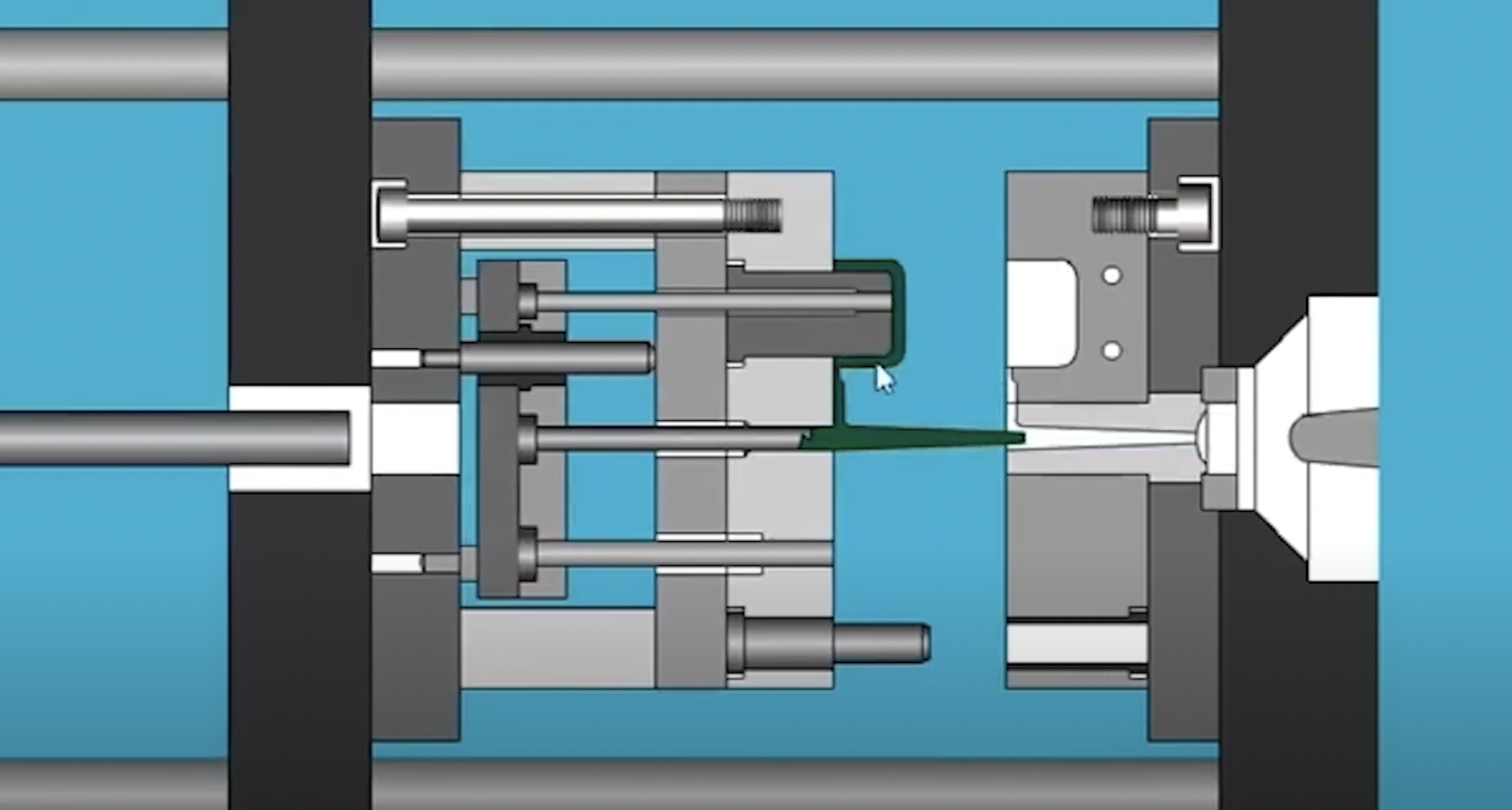
😎 In a tooling mold, ejector pins and core pins are indispensable components, each performing distinct roles. 📣
🤔 Today, I'd like to share some fundamental information about these two essential parts, particularly for beginners like myself. While they primarily serve different purposes in a mold, I still find myself wondering if there are aspects where their functions overlap.
👩💻 Here is what I've gathered from my research:
🔔 Ejector Pins:
Function: hashtagEjectorpins are designed to push the finished molded product out of the mold cavity once the molding process is complete.
Location: Typically, ejector pins are located in the ejector half of the mold. They are positioned to align with specific features or areas of the molded part.
Action: When the mold opens after the plastic has solidified, the ejector pins move forward, pushing the molded part out of the cavity and allowing for easy removal.
🔔 Core Pins:
Function: hashtagCorepins, on the other hand, create voids or cavities within the molded part. They help form internal features or details of the part.
Location: Core pins are usually located in the core half of the mold. They define the inner shape of the molded product.
Action: During the molding process, molten plastic flows around the core pins, taking the shape of the internal features. Once the plastic solidifies, the mold opens, and the core pins retract, leaving the molded part with the desired internal structure.
Both ejector pins and core pins are crucial for achieving the desired shape and functionality of the molded product. They contribute to the efficiency and precision of the injection molding process. 👩🏫
While ejector pins and core pins typically have distinct functions, there can be cases where their roles overlap or they seem to serve a similar purpose. ❤️
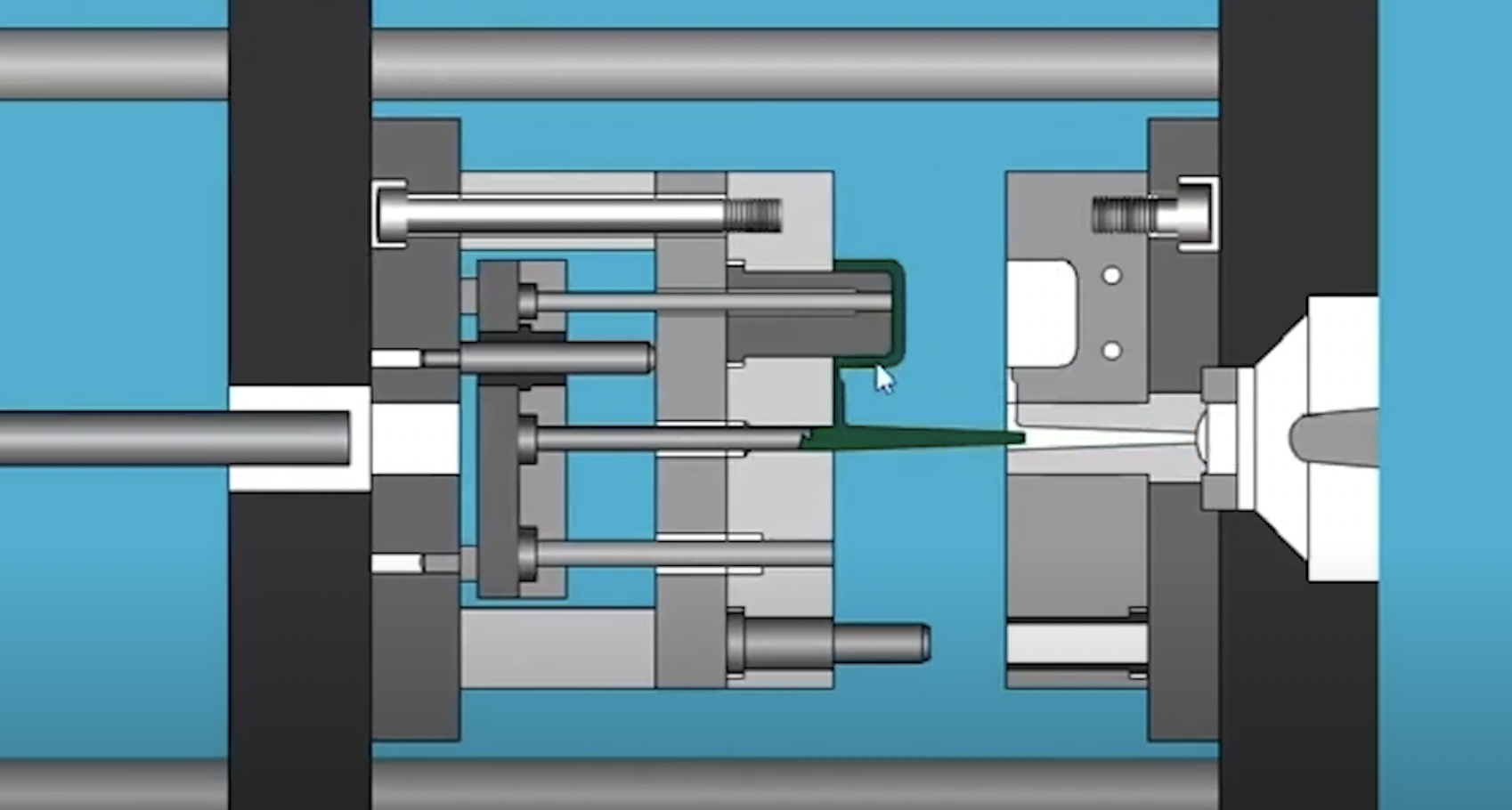
💡 Complex Molds:
In intricate molds with multiple sliders, lifters, and complex part geometries, the functions of ejector pins and core pins can become more intertwined. Some core pins may also play a role in ejecting the part, especially if they have tapered or undercut features that assist in the ejection process.
🔎 Internal Lifters:
In molds with internal lifters or collapsible cores, certain core pins may act as both shaping elements and aids in the ejection of the molded part.
📕 Part Release Assistance:
Ejector pins might be strategically placed to assist in the release of specific features created by core pins, ensuring that no undercuts or complex geometries impede the ejection process.
📒 While these examples illustrate situations where there might be some overlap, it's important to note that the design and placement of ejector pins and core pins are typically optimized for their primary functions.
The selection and arrangement of these components depend on the specific requirements of the molded part and the complexity of the mold design🤝

hashtagtoolinglearning
Following a discussion with my colleague, I learned that ejector sleeves are not necessary for every ejector pin. Instead, their usage is often dictated by the part's design. Specifically, if the part incorporates a column design, it is advisable to use ejector sleeves. This valuable information provides a reference point for my understanding of mold design intricacies. Below detailed information for reference.
The decision to use ejector sleeves for each ejector pin depends on the specific requirements of the molding application and the design of the mold. In many molds, only certain ejector pins, particularly those in contact with visible or critical surfaces of the molded part, may have corresponding ejector sleeves.
Here are some factors to consider:
Part Geometry: If the molded part has complex geometry or features that are sensitive to surface imperfections, ejector sleeves may be used for specific ejector pins that come in direct contact with those areas.
Cosmetic Requirements: If the molded parts have strict cosmetic requirements, ejector sleeves may be employed to minimize the risk of surface defects caused by ejector pin contact.
Material Type: The type of material being molded can influence the decision. Softer or more delicate materials may benefit from the use of ejector sleeves to prevent damage during ejection.
Mold Design: The overall design of the mold, including the layout of ejector pins and the molding process requirements, will influence whether ejector sleeves are used universally or selectively.
In summary, ejector sleeves are strategically applied to ejector pins based on the specific needs of the molding process and the desired quality of the molded parts. It's a design decision made by considering factors related to part aesthetics, material characteristics, and overall molding requirements.
In a tooling mold, an ejector sleeve is a component designed to facilitate the ejection of molded parts from the mold cavity. It is a cylindrical sleeve typically positioned in the ejector plate and aligned with the ejector pins. The primary purpose of the ejector sleeve is to guide and support the ejector pins during the ejection process.
Here's how it works:
Alignment and Support: The ejector sleeve provides a precise and stable guide for the ejector pins. It ensures that the pins move vertically and accurately within the mold.
Ejection of Molded Parts: When the mold opens after the completion of the injection molding cycle, the ejector pins, guided by the ejector sleeves, move forward into the mold cavities. This movement helps push the molded parts out of the cavities.
Preventing Damage: The ejector sleeve helps distribute the ejection force evenly, preventing damage to the molded parts or the mold itself. It ensures a smooth and controlled ejection process.
Durability: Ejector sleeves are often made from wear-resistant materials to withstand the repetitive movements and forces involved in the ejection process.
In summary, the ejector sleeve plays a crucial role in the successful and efficient ejection of molded parts from the mold, contributing to the overall precision and reliability of the injection molding process.