Exploring Fillets and Chamfers: The Subtle Differences in Machining
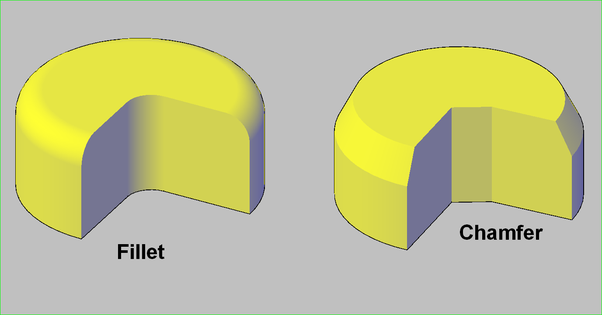
In engineering design and manufacturing, fillets and chamfers are two common yet often confused concepts. While both are used to address edges, their functions and forms have subtle differences. Let's delve into the differences between fillets and chamfers, as well as their varied applications in machining and design.
Fillets:
Fillets refer to rounding off the corners or edges between two surfaces with circular or curved shapes. The primary purpose of fillets is to reduce sharp edges, alleviate stress concentrations, and enhance the strength and durability of components. In design, fillets are typically represented by the radius, denoted as 'R', which signifies the radius of the fillet.
In machining, fillets can be achieved through various processes, including milling, grinding, and injection molding. Fillets offer a smoother appearance, making them suitable for components that require aesthetic appeal and comfortable handling.
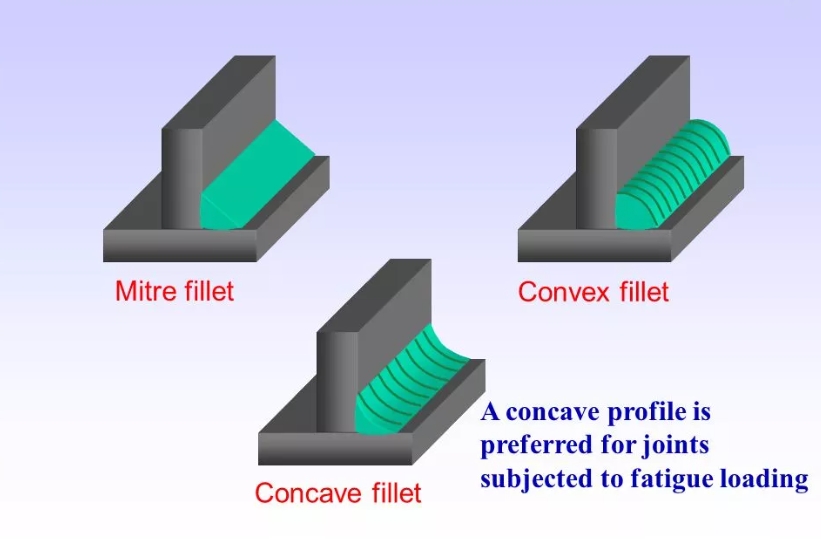
There are three types of fillet mechanisms: miter fillets, concave fillets, and convex fillets. On the inside, the fillet is concave, while on the outside, the fillet is convex. Engineers use fillets to reduce stress on parts. Therefore, rounded corners help distribute stress over a larger surface, preventing rapid deformation of stressed components.
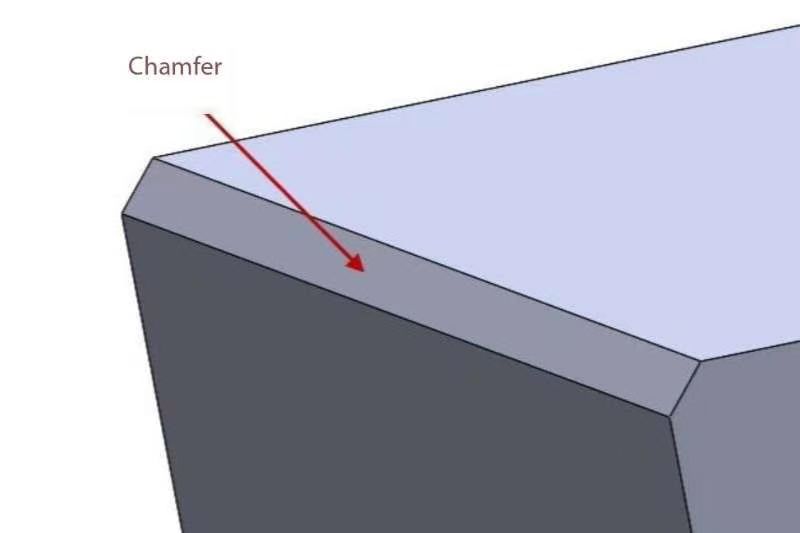
Chamfers:
Chamfers involve creating angled or flat surfaces between two edges. The primary function of chamfers is to simplify assembly, reduce abrasion, and improve the reliability of components. In design, chamfers are typically defined by the length of the edges and the angle of inclination.
Chamfers are commonly created at a 45-degree angle, although they can be adjusted according to specific requirements. In machining, chamfers are often achieved through milling, cutting, or grinding methods. Chamfers offer a more linear appearance, suitable for simplifying edges and enhancing component assembly.
Differences Between Fillets and Chamfers:
1.Shape Difference: Fillets are circular or curved, while chamfers are angled or flat.
2.Different Functions: Fillets primarily reduce stress concentrations and increase strength, while chamfers simplify assembly and reduce abrasion.
3.Appearance Characteristics: Fillets have a smoother appearance, whereas chamfers appear more linear.
4.Machining Methods: Although both can be machined through milling, cutting, or grinding, the appropriate machining method should be selected based on design requirements and workpiece characteristics.
Application scenarios of fillet:
1.Stress concentration reduction: Filleting can reduce stress concentration on the edge of the part and reduce the risk of part breakage due to stress concentration.
2.Increase part strength: By adding fillets, you can increase the overall strength and durability of the part, especially for parts that are subject to frequent force or vibration.
3.Appearance and feel: Rounded corners can make the edges smoother, more beautiful in appearance, and provide a more comfortable feel, suitable for parts that need to be touched or operated.
4.Lower processing costs: Generally, it is easier and cheaper to process fillets than chamfers, so it has more advantages in terms of cost and efficiency.
Application scenarios of Chamfer:
1.Assembly and installation: Chamfers simplify the assembly process of parts, making them easier to align and connect, especially for parts that require manual or automated assembly.
2.Prevents impacts and damage: Chamfers can reduce impacts and damage between parts, especially if they are moving or in contact with other parts.
3.Reduce bayonet and clamping: Chamfering can prevent parts from getting stuck or damaged in the fixture, improving the stability and efficiency of the machining process.
4.Beautiful appearance: Chamfering can make the edge of the part look neater and more professional, especially suitable for products that require a beautiful appearance.
Understanding the differences between fillets and chamfers is crucial in ensuring product quality and performance in design and manufacturing. Choosing the appropriate edge treatment based on specific design requirements and application scenarios will enhance the functionality and aesthetics of components.