Hot Runner vs. Cold Runner Molds
Injection molding is a widely used process to produce consumer goods from plastic, and many of our manufactured products are injection molded.
From auto parts to appliance housings and cell phone cases, injected molded plastic parts are all around us.
There are several injection mold types. However, based on the temperature held by the runner and the mold, there are two mold systems: hot runner and cold runner.
Each mold system uses a different mechanism which affects plastic fabrication differently.
As a result, there is a need for a proper understanding of the hot runner mold vs cold runner mold comparison before selection.
This article does the hot runner vs cold runner injection molding comparison by introducing both systems, how they work, and their differences.
Furthermore, it shows how to choose the right mold for your project.

How Cold Runner Molds Work
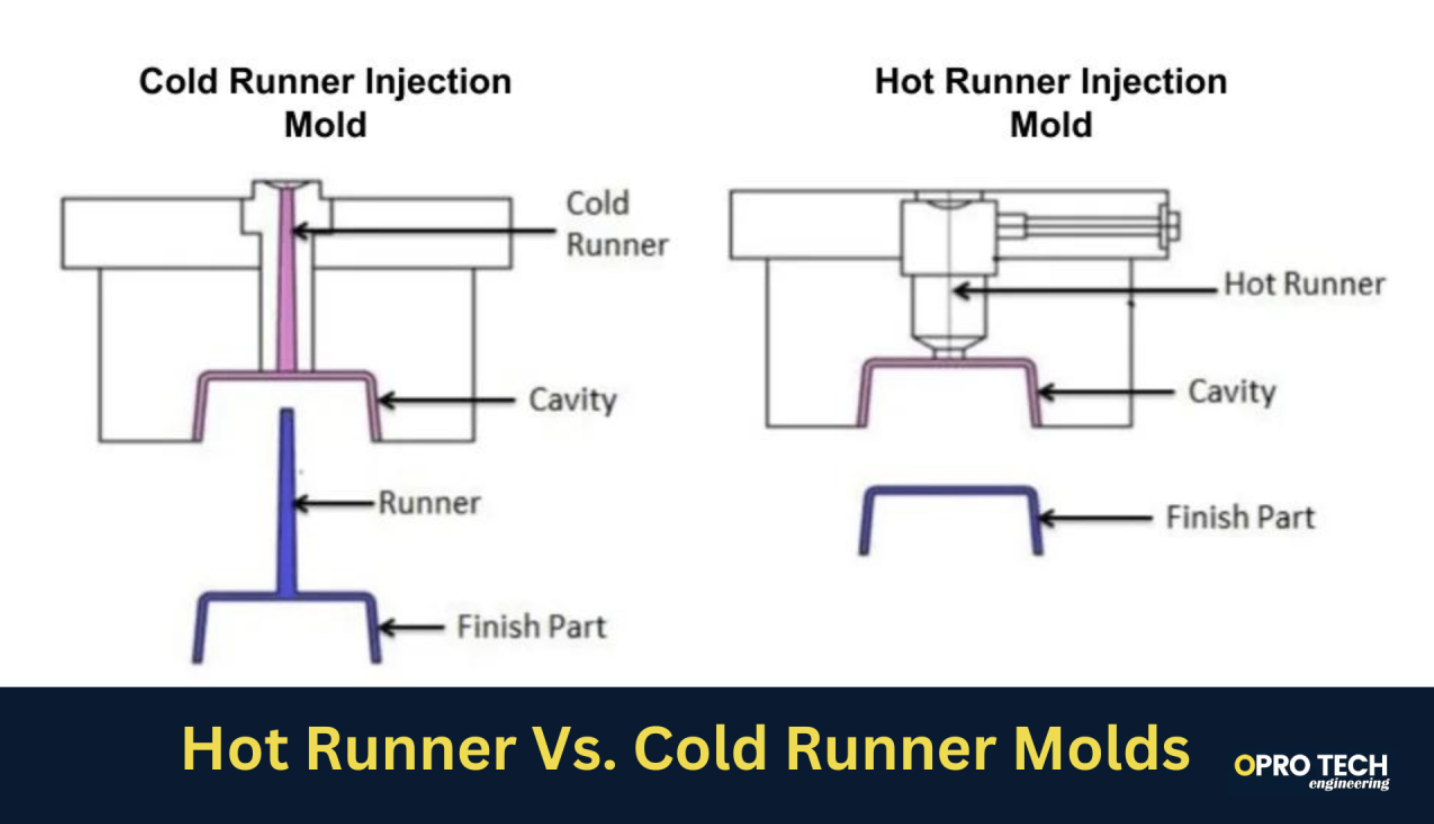
In cold runner molds, plastic is injected from a nozzle on the injection molding press into a sprue bushing, where the material flows through unheated channels and then finally through an injection molding gate.
Because the material from the nozzle is not heated along the way, this type of mold is called a cold runner.
The entire sprue is many times larger than the part, which is cooled and ejected from the mold with excess material attached. Known as scrap, this excess material must be cut away and reground to be reused or thrown away.
Compared to hot runner molds, cold runner molds produce significantly more scrap.
How Hot Runner Molds Work
With hot runner molds, plastic material is injected from into a heated plate and nozzle system called a manifold. This material is then kept at its melting temperature until it reaches the mold.
This approach allows for better temperature control and supports greater control over parameters such as pressure and time.
Hot runner molds produce considerably less scrap than cold runner molds, and when valve gating is used, there’s almost no scrap at all.
Comparing Hot Runner and Cold Runner Molds
That said, you’ve got to consider more than just scrap when determining whether to use a hot runner or a cold runner for your injection molding project.

Above Picture credited: fictiv
Types Of Cold Runner Systems
There are two types of cold runner mold systems based on the number of mold plates:
· Two Plate Cold Runner System
The two-plate cold runner system comprises two plates with the stationary mold containing the sprue, runners, gate, and cavities.
It is the fastest, simplest, and least costly cold runner system.
However, the runner is attached to the final product and should be cut off.
· Three Plate Cold Runner System
A three-plate cold runner system is similar to the two-plate system. However, the three-plate injection mold is flexible with an additional runner plate.
Furthermore, there is no need to cut the runner from the injection molded part, and the mold does not require an ejection system for part removal.
3 plate injection mold is friendlier and more flexible.
They are the most suitable for working with products with complex designs, and they are a lower-cost alternative to hot runner systems. Disadvantages of this injection mold include long cycle time, complex tool design, and high material waste.

Considerations When Choosing the Hot Runner Molds
Choosing the right hot runner mold should be based on price, delivery time, and quantity.
However, more important factors rest on the technical aspect of the runner system. Below are a few you should take note
– Injection Pressure
Due to the consistent temperature of the molten plastic, while passing through the manifold system, the injection pressure drop is low. As a result, it’s important to ensure proper mold flow simulation during injection mold design when working with all materials for injection molding, especially those with poor melt-flow performance.
– Heating
The heating component can be internal or external. External heating systems are suitable for thermosensitive materials. On the other hand, internally heated systems are suitable for other plastic polymers.
– Gate Type
Every material and product design requires a unique gate design. Therefore, consider factors such as gate mark, location, and injection of material types when making the gate.
– Standard or Custom-Made System
Choosing from a standard or custom-made system depends on your requirements.
On the one hand, the standard system has standard components and dimensions.
Consequently, they are the best choice due to cost, delivery time, and maintenance.
On the other hand, custom-made systems are ideal for achieving products with unique designs.
– Types of Plastic Processing
The plastic polymer you are working with also plays an important role in the choice. For example, glass-reinforced plastic needs molds having gate inserts with good wear resistance or an external heat system runner.
– Runner Size
The runner size plays a critical role in the system’s performance. Getting it wrong can lead to the degradation of the final components or incomplete filling. Some factors such as the pressure drop, residence time, operation temperature, and shear rate and frequency can determine the size of the runner.
– Multi-Zone Temperature Control
When working with a large and complex system or a thermosensitive plastic, ensure you use a multi-zone temperature control system to account for heater quality and heat loss.

Consideration When Choosing the Cold Runner Mold
Below are the important factors you should consider when choosing a cold runner mold.
– Nozzles
Choose a nozzle that is not welded to prevent penetration of particulates into the water jacket.
– Nozzle Tips
The type of nozzle tips depends on the manufacturers. For example, some mount the nozzle tips securely to the nozzle’s end, while others use spring-loaded nozzle tips because it allows for the mold’s thermal expansion during heating.
– Runner Manifolds
The runner manifold should have a split plate design to ease disassembling and cleaning. Other designs, such as the gun-drilled runner, can lead to “dead spots,” making the mold harder to clean.
– Piston Assembly
Using gun-drilled air passageways can eliminate the nozzle’s need for air hoses and barb fitting to prevent airline damage and eliminate connection errors.
– Pneumatic Connections
The better cold runner mold should either have an external airline or an air terminal box with a quick disconnect coupler.

Hot Runners vs. Cold Runners for Your Project
Do you need a hot runner mold or a cold runner mold for your next injection molding project?
This decision is a lot easier to make when you explain to your manufacturing partner which factors are most important, and the expected number of parts that you’ll run at a given time.
Opro-tech: Your Injection Molding Partner
Opro-tech is the right partner who can help you make the right choice when it comes to hot runners or cold runners for your next project.
We are also an ISO 9001:2015 company with advanced facilities and teams that can handle your project.
Contact me at xiu@opro-tech.com and our injection molding experts guide you to make sure your designs are optimized and our manufacturing partners are incredibly skilled.
