What is chromate conversion coating and its role in post-processing of machined products?
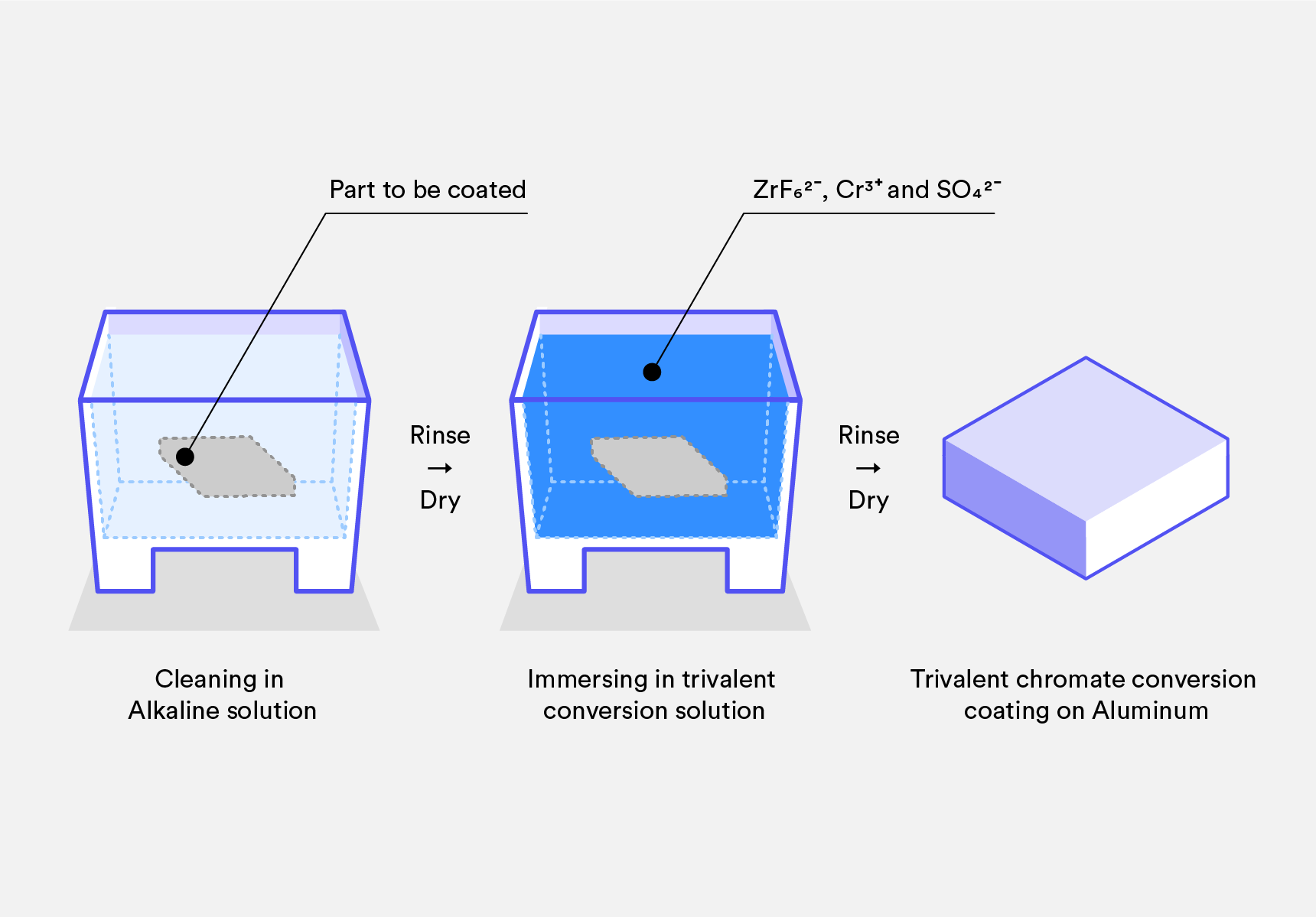
Chromate conversion coating refers to a thin film formed on the surface of machined products through chromate treatment. This film is typically composed of chromium oxide or other chromium compounds, exhibiting certain hardness and corrosion resistance, serving several crucial protective functions. In the post-machining treatment of products, the formation of chromate conversion coating serves the following purposes:
Corrosion Prevention: Chromate salts can form a protective oxide or conversion coating, aiding in preventing corrosion of the metal surface. This is essential for protecting mechanical components from corrosion when exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Hardness Enhancement: After chromate treatment, a surface may develop a high-hardness oxide layer, thereby increasing the hardness of metal components. This is beneficial for improving the wear resistance and fatigue performance of the parts.
Surface Quality Improvement: Chromate treatment can enhance the smoothness and evenness of the metal surface, making it more suitable for applications with high surface quality requirements, such as precision mechanical components.
Increased Wear Resistance: By forming a high-hardness oxide film, chromate treatment helps improve the wear resistance of metal components, extending their operational lifespan.
Enhanced Oxidation Resistance: Chromate-treated metal surfaces may exhibit improved oxidation resistance, allowing them to maintain satisfactory performance in high-temperature or oxygen-rich environments.
In summary, the formation of chromate conversion coating in the post-machining treatment of products provides corrosion prevention, hardness enhancement, surface quality improvement, increased wear resistance, and enhanced oxidation resistance.