What is the difference between heat treatment and cold treatment?
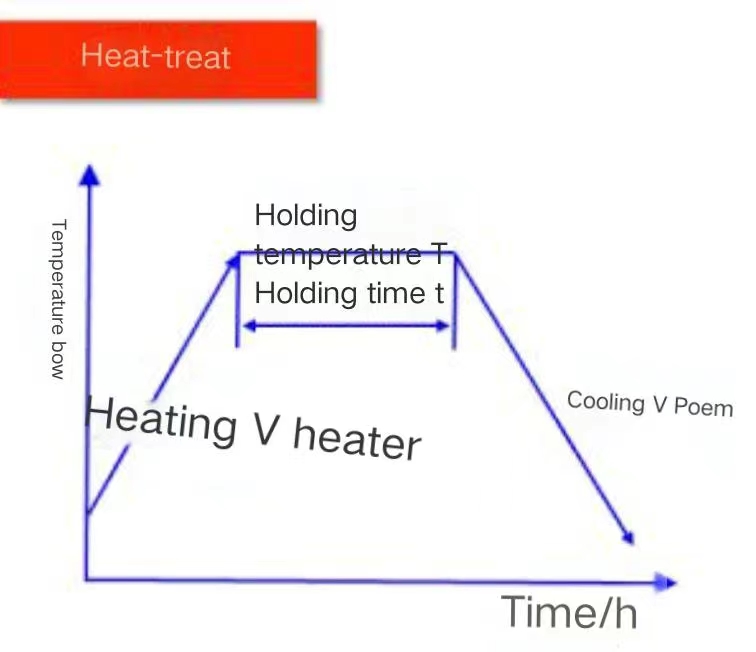
Cold treatment and heat treatment of machined products are two different processes. They mainly change the properties of the material by controlling the temperature and time of the material.
Here are some of the main differences between them:
1.Temperature range:
Cold treatment: It is carried out at room temperature or lower temperature, generally below the plastic deformation temperature of the material.
Heat treatment: Requires higher temperatures, usually above the temperature at which the material's grains rearrange, and can reach the material's solid-state phase transition temperature.
2.Purpose:
Cold treatment: The main purpose is to improve the hardness and strength of the material and reduce the plastic deformation of the material.
Heat treatment: Designed to improve the mechanical, thermal and physical properties of materials, including increasing hardness, strength, toughness and wear resistance.
3. Process characteristics:
Cold treatment: including cold rolling, cold drawing, cold forging and other processes, usually does not involve heating process.
Heat treatment: Including processes such as quenching, tempering, and annealing, which involve heating the material to a certain temperature and then achieving the required properties through different cooling rates.
4. Effect:
Cold treatment: Makes the material harder and brittle, but may reduce its toughness.
Heat treatment: Able to balance the hardness, strength and toughness of a material to achieve optimal performance.
5.Application fields:
Cold treatment: usually used to increase the hardness of metal, such as in the manufacture of sheets, wires, etc.
Heat treatment: Used extensively on a variety of metals and alloys, including steel, aluminum, copper, etc., to tune their properties to meet specific engineering needs.
Generally speaking, cold treatment and heat treatment are two different processes, and the choice of which one to use depends on the type of material, the properties required and the application area of the final product.