What is CVD?
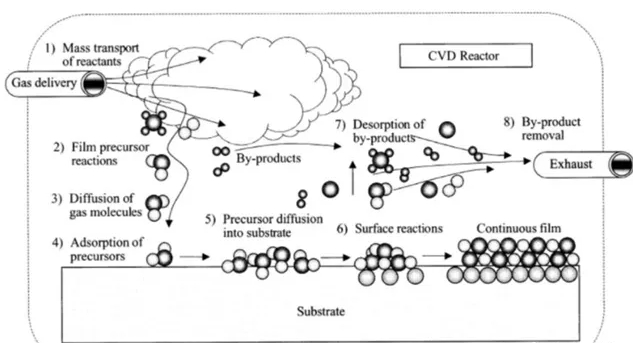
In the field of surface technology and coating technology, CVD (chemical vapor deposition) is an important process that deposits a uniform, dense film or coating on the surface of a material by introducing gas precursors in a high-temperature environment. This article will delve into the definition, principles and application areas of CVD, revealing its key role in modern industry.
Definition of CVD:
CVD is a surface deposition technology that creates a uniform coating by forming a chemical reaction on the surface of the material. This process occurs in high-temperature environments, typically between 700°C and 1,000°C. The main principle is to introduce gas precursors to cause chemical reactions on the surface to form the required solid film or coating.
The principle of CVD:
Gas Precursor Introduction: A gas precursor, usually a gaseous or volatile liquid, is introduced into the reaction chamber.
Chemical Reaction: In a high-temperature environment, gas precursors undergo chemical reactions to produce solid products.
Deposition: The solid product is deposited on the surface of the material to form a dense, uniform coating.
Exclusion of reactants: The waste gas after the reaction is eliminated through the system to maintain the balance of the reaction.
As a core technology of surface technology, CVD has contributed to the progress and innovation of multiple industrial fields through its unique principles and wide range of applications. Its deposition process in a high-temperature environment makes it ideal for preparing high-performance coatings and films. When using CVD technology, strict control of reaction conditions and careful selection of gas precursors are key to ensuring quality and effectiveness.