What are expandable cavities?
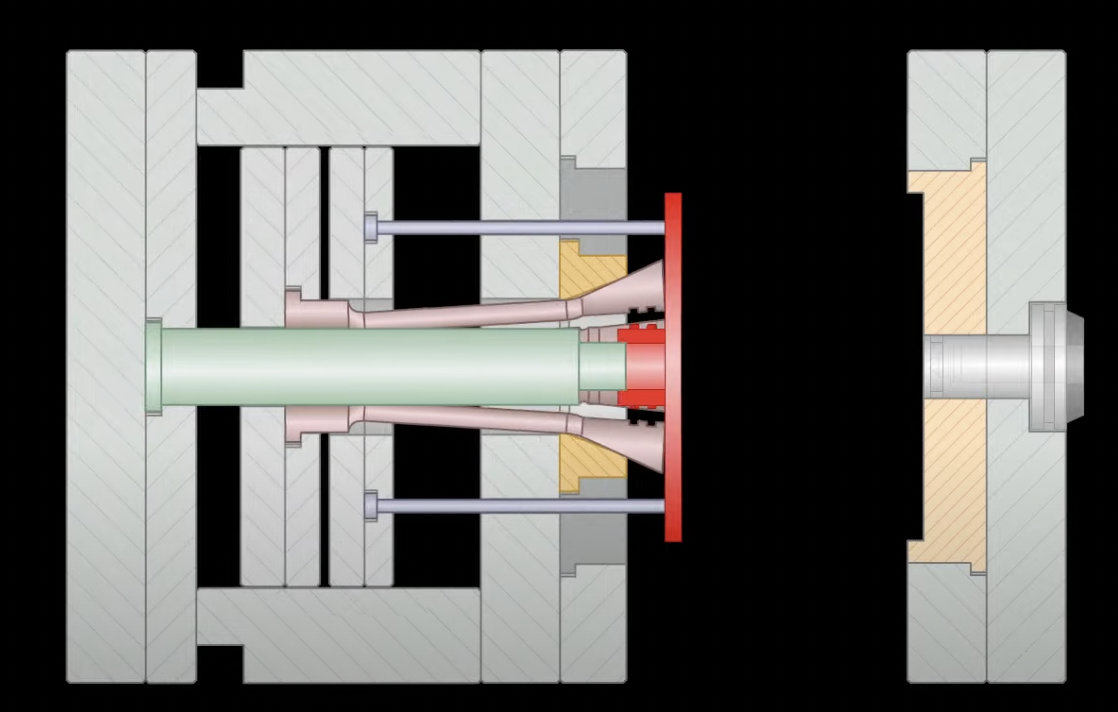
🤔 As part of my ongoing exploration into hashtagtooling mold technologies, I have been learning the concept of expandable cavities. Through visual aids such as images and videos, it becomes apparent that expandable cavities are strategically employed when dealing with intricate features like undercuts or grooves in plastic parts. 🤔
😫 But based on some information, it says the use of an expandable cavity in a tooling mold is not typically associated with managing undercut or groove systems in plastic parts. The primary purpose of an expandable cavity is to provide flexibility in adjusting the overall size of the mold cavity during the molding process. This flexibility is often utilized to accommodate variations in material shrinkage or to optimize part dimensions. 😕 🤔
😊 I would appreciate your assistance in confirming the accuracy of the information I've come across. Your guidance in clarifying this matter would be greatly valued. Thank you for your consideration. 🙍♀️ ❤️
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGHy2udaVdc

Below information for reference.
An expandable cavity in a tooling mold refers to a design feature that allows the mold cavity to be adjusted or expanded during the molding process. This is typically used for certain applications where the molded part requires flexibility in its dimensions or when dealing with variable factors like material shrinkage.
Advantages of an Expandable Cavity:
Flexibility: An expandable cavity provides the ability to adjust the size of the cavity during the molding process. This can be beneficial when dealing with materials that have variable shrinkage rates or when precise control over part dimensions is critical.
Tolerance Compensation: It allows for real-time compensation for variations in material properties or process conditions, ensuring that the final parts meet specified tolerances.
Optimized Part Quality: The ability to adjust the cavity size based on real-time conditions contributes to better control over part quality, reducing the likelihood of defects.
Material Savings: By accommodating material shrinkage more precisely, an expandable cavity can help reduce material waste.
Comparison with a Standard Cavity:
Standard Cavity: In a traditional mold with a fixed cavity, the tooling is designed for a specific part size, and adjustments cannot be made during the molding process. This may work well for stable processes and materials with consistent shrinkage rates.
Expandable Cavity: Offers greater adaptability, making it suitable for applications where precise control over dimensions is crucial or when dealing with materials that exhibit variations in shrinkage.
The choice between a standard and an expandable cavity depends on the specific requirements of the molding project and the characteristics of the material being processed.