MIG Welding: Fusion for Modern Manufacturing
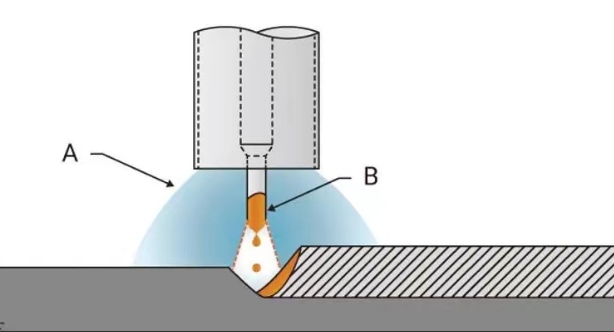
MIG welding, or gas metal arc welding (GMAW), is a modern, advanced welding technology that achieves precise fusion of metals by continuously replenishing wire electrodes and shielding gases.
Key components:
Wire Electrode: MIG welding uses a consumable wire electrode, usually solid wire or flux-cored wire. The welding wire is continuously powered through the welding gun.
Welding Torch: A welding torch is a handheld tool powered by a wire electrode. It also contains a trigger to control wire release and in some cases a shielding gas jet
Power supply: The power supply provides the electrical energy required for the arc, providing the required voltage and current to form the welding process.
Shielding gas: Use shielding gas, usually a mixture of upper gas and high pressure, to protect the welding pool during the welding process and prevent atmospheric pollution.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=twUAa5LWUvk
Working principle:
Wire Electrode: The wire electrode is continuously powered from the wire spool and delivered to the workpiece.
Arc formation: When the welding wire comes into contact with the workpiece, an arc is formed. The arc generates high temperatures that melt the wire and workpiece.
Release protective gas: Release protective gas at the same time to form a protective atmosphere to prevent atmospheric oxidation and other effects on the weld.
Welding pool formation: A welding pool is formed by the combination of the welding wire and the molten metal of the workpiece. After cooling, the weld pool solidifies to form a reinforced weld.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gc9fBVq9NlE&t
Application fields: It can not only weld ordinary structural steel, but also weld various stainless steels, heat-resistant steels, heat-tough steels, special alloys, aluminum alloys, magnesium, nickel, copper, and oxide alloys with strong chemical affinity. This welding method can be used in every position in space and is quite common in the production of various products (such as tables and chairs, motorcycles, bicycle racks) or in shipbuilding, car barrels, machine workshops, production lines, etc.