CNC Precision Machining and Rough Machining: The Dual Wings of Industrial Manufacturing
In today's industrial manufacturing field, CNC precision machining and rough machining are two crucial machining methods that together constitute the dual wings of modern manufacturing. These two machining methods each have unique characteristics and advantages, playing irreplaceable roles at different stages, providing efficient, precise, and reliable solutions for product manufacturing.
CNC Precision Machining: Precise Digital Control
CNC precision machining is a computer-controlled machining technique that precisely controls machining equipment for processes such as cutting, drilling, and milling based on pre-programmed instructions, achieving high-precision requirements for workpiece dimensions, shapes, and surface quality.
The key advantage of CNC precision machining lies in its high automation and precision. Through digital control systems, operators can easily adjust machining parameters to achieve precise machining of complex parts, improving production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, CNC precision machining also offers good repeatability and consistency, ensuring stability and reliability in mass production scenarios.
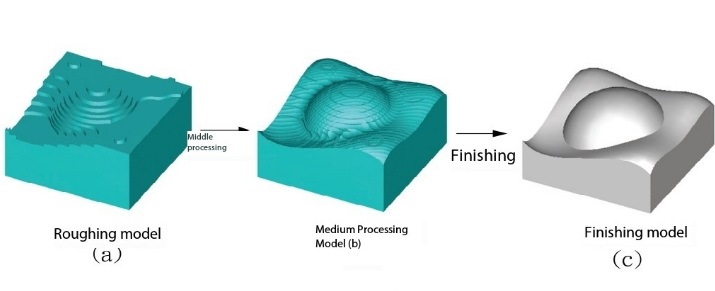
Rough Machining: Vital Stage for Material Removal
Rough machining is a vital stage in the manufacturing process for removing materials, primarily aiming to quickly form initial workpiece shapes and dimensions, laying the foundation for subsequent precision machining and processing procedures. Compared to precision machining, rough machining typically emphasizes the speed and efficiency of material removal, with relatively lower requirements for surface quality and accuracy.
In rough machining, common machining methods include milling, turning, and drilling, often employing high-speed cutting and large feed rates to rapidly remove excess material and form initial contours. Rough machining not only reduces the difficulty and complexity of subsequent machining processes but also saves machining time and costs, improving production efficiency and resource utilization.
The difference between finishing and roughing milling cutters
Geometric Shape of Tool:Precision Machining End Mills typically have more teeth, closer tooth spacing, and sharper cutting edges. This design helps to provide higher surface quality and more precise cutting. Rough Machining End Mills usually have fewer teeth, larger spacing between teeth, and rounder cutting edges. This design allows for more efficient removal of a large volume of material to improve machining efficiency.
Tool Material:For precision machining end mills, materials with higher hardness and better wear resistance are often chosen to ensure stable cutting performance and long tool life during high-speed machining.For rough machining end mills, in addition to wear resistance, tool toughness and strength are also considered since rough machining may involve significant impact and vibration.
Cutting Parameters:In precision machining, smaller feed rates and cutting depths are often used to ensure cutting accuracy and surface quality.In rough machining, larger feed rates and cutting depths may be used to quickly remove material and improve machining efficiency.
Machining Strategy:Advanced machining strategies like High-Speed Machining (HSM) are often used in precision machining to maximize machining efficiency and surface quality.
In rough machining, the focus may be more on machining speed and material removal rate, thus higher feed rates and larger cutting depths may be employed.
CNC precision machining and rough machining, as integral components of modern industrial manufacturing, provide reliable machining solutions for various product manufacturing needs. They not only improve production efficiency and product quality but also drive technological progress and development in the manufacturing industry. With continuous innovation and technological advancement, CNC precision machining and rough machining are expected to continue playing important roles in the future, bringing a brighter future for industrial manufacturing.