What is the function of support pillar in tooling mold and what material should be ?
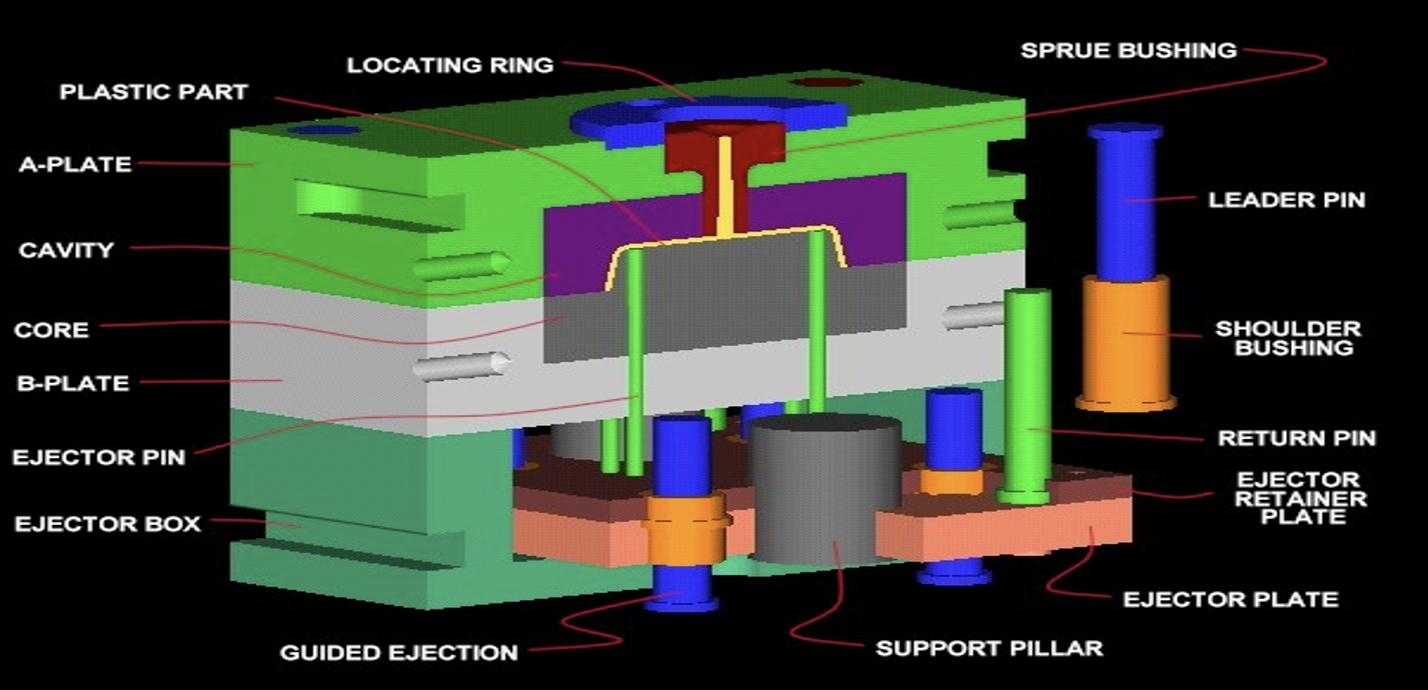
Support pillars, also known as mold pillars or mold supports, play a crucial role in the construction and operation of tooling molds used in various manufacturing processes such as injection molding.
As a beginner in mold design and fabrication, understanding the basics of support pillars is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of molds. So let's dive in and learn a little bit.
Support pillars are vertical columns strategically placed within the mold cavity to provide reinforcement and stability, particularly in large or complex molds where the risk of deformation or misalignment is higher. These pillars help distribute the forces exerted during the molding process, minimizing deflection and maintaining precise dimensional accuracy in the molded parts.
While this introduction provides a beginner-level overview of support pillars, there's always more to learn from experienced professionals in the field. If you have insights or tips to share about support pillars or mold design in general, please feel free to leave a comment below. Your contributions will enrich our understanding and benefit fellow learners in the community.

Support pillars serve several important functions in tooling molds:
- Structural Support: Support pillars bear the weight of various mold components, including the core, cavity, and slides. They ensure that the mold remains rigid and stable during operation, preventing deformation or misalignment that could compromise the quality of the molded parts.
- Alignment: Support pillars help align and maintain the proper positioning of the mold components. They ensure that the core and cavity maintain precise alignment throughout the molding cycle, which is crucial for producing accurate and consistent parts.
- Heat Dissipation: During the molding process, heat is generated due to the interaction between the molten material and the mold surfaces. Support pillars help dissipate this heat, preventing overheating and ensuring uniform cooling of the mold.
- Pressure Distribution: In molds where high injection pressures are applied, support pillars help distribute the pressure evenly across the mold surface. This prevents localized stress concentrations and minimizes the risk of mold failure or damage.

Support pillars in tooling molds require materials that offer high strength, durability, and heat resistance to withstand the demanding conditions of the molding process.
The choice of material depends on various factors such as the application, molding environment, and specific requirements of the mold. Some common materials used for support pillars include:
1. Tool Steel: Tool steels such as P20, H13, or S7 are popular choices for support pillars due to their excellent wear resistance, toughness, and machinability. These steels can withstand high pressures and temperatures encountered during injection molding and are suitable for use in a wide range of molding applications.
2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel grades like 420 or 440 are preferred for molds requiring corrosion resistance or those used in food-grade or medical applications. Stainless steel offers good mechanical properties and can withstand repeated cycles of molding without degradation.
3. Aluminum: Aluminum alloys such as 7075 or 6061 are lightweight yet strong materials commonly used for support pillars in molds where weight reduction is critical or for molds used in low-pressure molding processes like rotational molding. Aluminum also offers good thermal conductivity, aiding in the efficient cooling of the mold.
4. Bronze or Brass: In certain specialized applications, bronze or brass alloys may be used for support pillars due to their excellent machinability, low friction properties, and resistance to wear. These materials are often chosen for molds producing abrasive or high-temperature materials.
5. Composite Materials: For molds requiring specific properties such as high stiffness, low thermal expansion, or reduced cycle times, composite materials reinforced with fibers like carbon fiber or glass fiber may be utilized for support pillars. These materials offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of the mold.

Support pillars are designed into tooling molds to provide structural support and stability, particularly in areas where there are large spans or heavy components. They help prevent deflection, warping, or deformation of the mold during the molding process, ensuring the accuracy and quality of the molded parts. Support pillars are typically incorporated in the following situations:
- Large Molded Parts: When molding large or complex parts with extensive surface areas, support pillars help distribute the clamping force evenly across the mold, reducing the risk of deformation or misalignment.
- Thin-Walled Parts: Thin-walled parts are susceptible to warping or distortion under pressure and heat during the molding process. Support pillars provide additional reinforcement to maintain the shape and dimensional accuracy of these parts.
- High-Pressure Molding: In high-pressure molding processes such as injection molding, support pillars help withstand the forces exerted by the molten material, preventing mold deflection and ensuring consistent part quality.
- Heat Transfer: Support pillars can also serve as conduits for cooling channels, enhancing heat transfer within the mold and facilitating faster cycle times.
The number of support pillars required for a specific tooling mold depends on various factors, including:
- Mold Size and Configuration: Larger molds or molds with complex geometries may require more support pillars to ensure adequate reinforcement and stability.
- Material Properties: The type of material being molded and its processing conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure) can influence the need for additional support to counteract material stresses.
- Mold Material: The choice of mold material (e.g., steel, aluminum) and its inherent strength characteristics can impact the design requirements for support pillars.
- Production Requirements: Considerations such as desired cycle time, part quality, and production volume may influence the design of support pillars to optimize mold performance and productivity.
Ultimately, the design and placement of support pillars in a tooling mold should be carefully evaluated during the mold design phase, taking into account the specific requirements of the molding process and the characteristics of the molded parts. Collaboration between mold designers, engineers, and molders is essential to determine the optimal configuration of support pillars to achieve the desired molding outcomes.

In conclusion, support pillars are indispensable components in the realm of tooling molds, serving to reinforce and stabilize mold structures during the manufacturing process. As we've explored in this beginner-friendly overview, these vertical columns play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy of molded parts, particularly in intricate or large-scale molding operations. While we've covered the basics of support pillars, there's always room to delve deeper into the nuances of mold design and fabrication.
If you have further questions, insights, or expertise to share about support pillars or any aspect of mold design, don't hesitate to reach out. Your contributions are invaluable in fostering a vibrant community of learners and practitioners in the field of tooling molds.
For more information or to engage in further discussion, feel free to contact us at danny@opro-tech.com. Let's continue to explore, learn, and innovate together in the exciting world of tooling molds.
Dan
Business development manager
Phone: +86 134 1699 5669
Skype: danny@opro-tech.com Factory add: No 39, Zhen an west road, Changan town , Dong guan city, China.
Injection Mold / CNC Machining / 3D Printing / Prototyping