What is a mold base? and how many parts does one mold base contain?
Hi, it's me. Danny, Market Development Manager at Oprotech Engineering. In our role, we believe in not only being sales professionals but also continually enhancing our technical expertise. We strive to learn and share insights gained through our experiences, aiming to provide valuable information that you may find helpful in your endeavors.
As I always said, I'm the beginner and always would be, I share what I learned from book, videos, oursource from network. So what I shared, I can't 100% garantee the absolute accuracy, but it's just what I learned and it make sense to me.
Ok now let's dive into the things what I got about mold base, thanks! And I would love to hear from you, please just leave a comment below or send me email at danny@opro-tech.com .

In tooling molds, the mold base serves as the foundation onto which various components of the mold assembly are mounted. It provides support and stability for the mold cavities, cores, and other components.
Mold bases are typically made from high-quality steel or aluminum to withstand the stresses and pressures of injection molding processes.
Some well-known brands of mold bases in the industry include:
- DME (Diversified Mold & Castings Co.)
- HASCO
- PCS Company
- Progressive Components
- Meusburger
These brands offer a range of standard and custom mold base options designed to meet the specific needs of injection molding applications. Depending on the requirements of the project, mold bases may vary in size, configuration, and features such as cooling channels, ejector systems, and alignment mechanisms. Choosing the right mold base is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the molding process.

A mold base typically contains the following parts, please tell me if I'm wrong about his.
- Clamping Plate: This plate is used to secure the mold to the injection molding machine.
- Guide Pins and Bushings: These components ensure proper alignment of the mold halves during operation.
- Sprue Bushing: The sprue bushing forms the entry point for molten plastic into the mold cavity.
- Ejector Plate: This plate contains the ejector pins or blades that push the molded parts out of the mold cavity after they have cooled.
- Core and Cavity Plates: These plates form the main cavities in which the plastic material is injected and shaped.
- Support Pillars: These pillars provide structural support for the mold assembly.
- Slide Retainers: These components hold the slides in place and prevent them from moving during operation.
- Cooling Channels: Channels machined into the mold base allow for the circulation of cooling water or other fluids to regulate the temperature of the mold.
- Return Pins and Bushings: These components ensure that the ejector system returns to its proper position after each cycle.
The number of parts included in a mold base can vary depending on the complexity of the mold design and the requirements of the molding process.
However, a typical mold base consists of several plates and components assembled together to form a complete mold assembly.

It's a common practice in the mold manufacturing industry for companies to purchase mold bases from specialized suppliers rather than producing them in-house. Well I thought that all the parts of a mold would be produced by mold facotry, which was wrong. Why don't we do this? There are several reasons for this:
- Specialization: Mold base suppliers specialize in manufacturing standardized mold bases that are compatible with various molding processes and machine types. They invest in specialized equipment, technology, and expertise to produce high-quality mold bases efficiently.
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing mold base production can be more cost-effective for mold manufacturers, especially for small to medium-sized companies. Purchasing standardized mold bases eliminates the need for expensive equipment, raw materials, and labor associated with in-house production.
- Time Savings: Mold base suppliers can deliver standardized mold bases quickly, reducing lead times for mold manufacturing projects. This allows mold manufacturers to focus on other aspects of mold production, such as cavity inserts and core components, which may require more specialized attention.
- Quality Assurance: Mold base suppliers often have stringent quality control processes in place to ensure that their products meet industry standards and specifications. By purchasing mold bases from reputable suppliers, mold manufacturers can ensure consistent quality and reliability in their final products.
Overall, outsourcing mold base production allows mold manufacturers to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency, ultimately benefiting both the manufacturer and their customers.

Usually there are two types of mold bases.
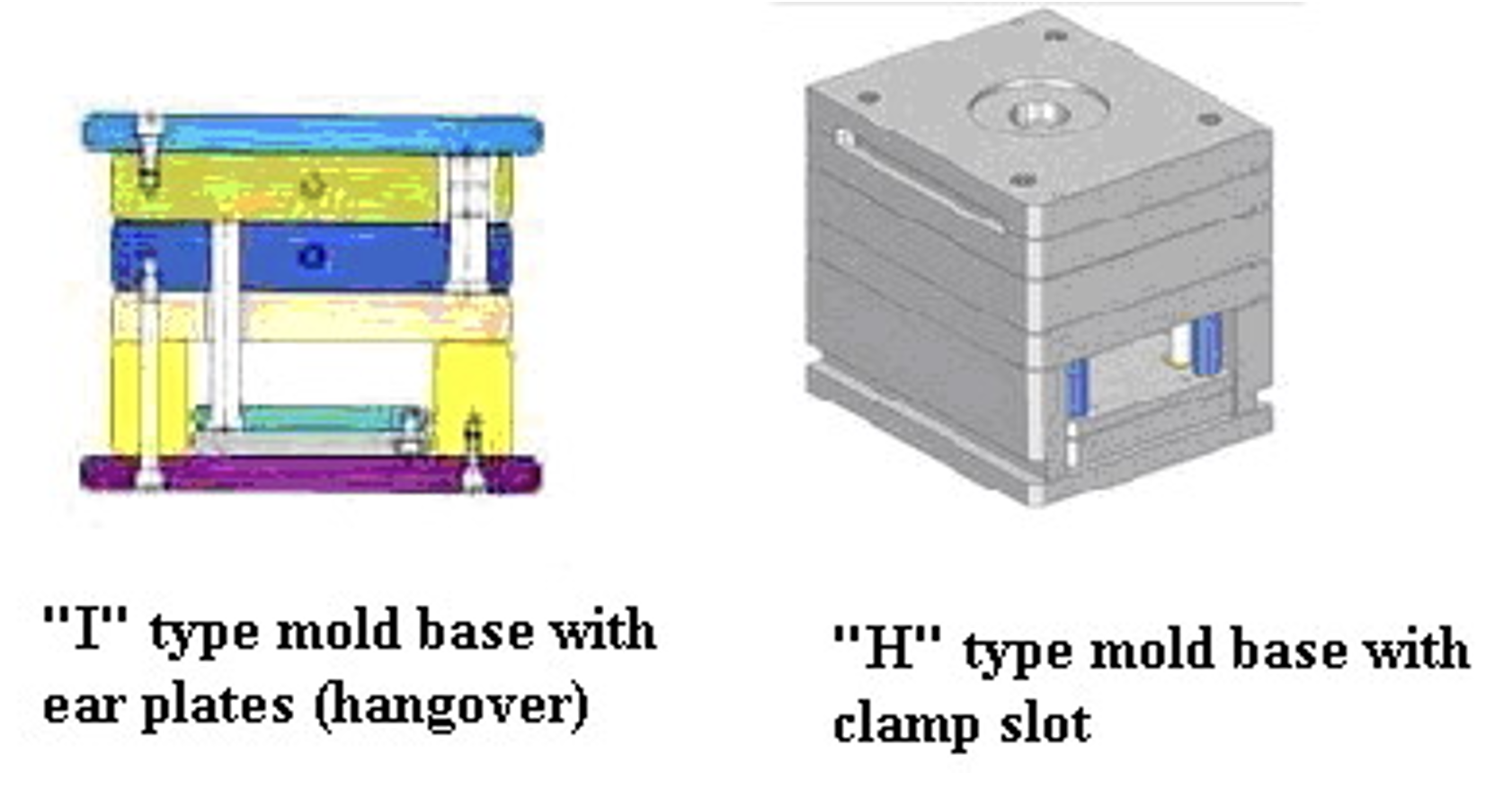
The H-type and I-type mold bases are two common configurations of standard mold bases used in the tooling mold industry:
- H-Type Mold Base:Description: The H-type mold base is named after its shape, which resembles the letter "H" when viewed from the side. It typically consists of two large plates (top and bottom) connected by support pillars or guide pins, forming a sturdy and rigid structure.Features:The H-type mold base offers excellent stability and rigidity, making it suitable for a wide range of molding applications. It usually has a larger footprint compared to other mold base types, providing ample space for mounting various components and accessories.H-type mold bases may come with standardized hole patterns, mounting options, and alignment features to facilitate easy assembly and compatibility with different molding machines.Applications: H-type mold bases are commonly used for medium to large-sized molds, especially in applications where dimensional accuracy and structural integrity are critical.
- I-Type Mold Base:Description: The I-type mold base is named after its shape, which resembles the letter "I" when viewed from the side. It consists of a single plate with machined features and inserts for mounting mold components.Features:The I-type mold base is more compact and streamlined compared to the H-type, making it suitable for smaller molds or applications with space constraints.It offers versatility in terms of customization, as mold makers can easily machine the single plate to accommodate specific mold requirements.I-type mold bases may have fewer standardized features compared to H-type bases, but they provide flexibility for adapting to different mold designs and configurations.Applications: I-type mold bases are often used for smaller or simpler molds, prototype molds, or molds with specialized requirements where customization is preferred over standardization.
Both H-type and I-type mold bases have their advantages and are chosen based on factors such as mold size, complexity, production volume, and specific project requirements. Understanding the differences between these two types can help mold designers and manufacturers select the most appropriate mold base for their applications.
Well except for the I type or H type mold base, customizing a mold base becomes necessary in several situations where the standard options may not meet the specific requirements of the mold design or the production process. Here are some scenarios where customization might be preferred:
- Complex Mold Designs: When the mold design is intricate or unconventional, standard mold bases may not provide the necessary features or configurations. Customizing the mold base allows for the integration of unique components, cavity layouts, or cooling channels required for complex mold designs.
- Specialized Applications: Certain applications, such as medical devices, automotive components, or consumer electronics, may demand precise tolerances, specialized materials, or specific features that are not available in standard mold bases. Customization enables the mold base to be tailored to the exact needs of the application.
- Non-Standard Part Sizes: If the parts to be molded have dimensions that deviate significantly from standard sizes, a custom mold base may be required to accommodate the unique part geometry and ensure proper alignment and functionality.
- High-Volume Production: For high-volume production runs, optimizing the mold design for efficiency, durability, and performance becomes crucial. Customized mold bases can be engineered to withstand the rigors of continuous production and maximize throughput.
- Integration of Auxiliary Equipment: In some cases, additional components or auxiliary equipment, such as hot runners, slides, lifters, or automation systems, need to be integrated directly into the mold base. Customization allows for the seamless incorporation of these elements into the mold design.
- Specific Mounting Requirements: If the mold needs to be mounted on a particular type of molding machine or requires specialized mounting provisions, customization of the mold base may be necessary to ensure compatibility and stability during operation.
Overall, the decision to customize a mold base is driven by the unique requirements of the mold design, production process, and end-use application. By opting for customization, mold manufacturers can tailor the mold base to their exact specifications, resulting in optimized performance, enhanced functionality, and improved overall quality of the molded parts.

Now here is a piece of more little inforamtion about ear plate/hangover and clamp slot.
The "ear plate" or "hangover" in a mold base refers to a part of the mold where additional features or structures are attached to facilitate handling, mounting, or clamping of the mold during operation. These features are typically designed to provide convenient points for securing the mold onto the molding machine or for handling it during assembly, disassembly, or maintenance.
Clamp Slot: The clamp slot is a specially designed groove or channel machined into the mold base to accommodate clamping devices or fixtures. These slots allow the mold to be securely fastened to the molding machine's platens or clamping mechanisms, ensuring proper alignment and stability during operation. Clamp slots come in different shapes and sizes to accommodate various types of clamps, bolts, or other fasteners used to hold the mold in place.

Ok that's all about the mold base I got here, in this journey through the realm of mold bases, I've uncovered essential insights for beginners like me. From understanding the components and types of mold bases to exploring customization options, I've delved into the foundational aspects of tooling molds.
Thank you social network. For further insights or to share your thoughts, drop us a message below or reach out at below:
Dan
Business development manager
Phone: +86 134 1699 5669
Skype: danny@opro-tech.com Factory add: No 39, Zhen an west road, Changan town , Dong guan city, China.
Injection Mold / CNC Machining / 3D Printing / Prototyping
"Danny's Learning Journey" video
offers a glimpse into the fascinating world of tooling molds through the eyes of a curious learner. Join Danny as he embarks on a quest to unravel the intricacies of mold design, production, and everything in between.
From beginner insights to expert discoveries, follow along as Danny shares his experiences, challenges, and newfound knowledge in the realm of manufacturing. It's a journey of growth, exploration, and endless possibilities in the ever-evolving landscape of tooling molds. 🛠️📚
Please click this to watch the video https://youtu.be/pbudoZureiQ