The Revolution of Ultrasonic Welding: Efficiency and Precision in Modern Manufacturing

In today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, the need for efficient and reliable joining methods has never been more critical. Ultrasonic welding has emerged as a transformative technology, offering unique advantages over traditional welding techniques. By harnessing high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations, this innovative process allows for rapid and robust bonding of materials, particularly in industries such as automotive, medical devices, and electronics. As companies strive for cleaner, stronger, and more efficient production methods, ultrasonic welding stands out as a vital solution in the quest for excellence.
Ultrasonic welding was developed in the late 1950s. The first commercial applications began in the 1960s, primarily for plastics. Over the years, the technology evolved, leading to its widespread use in various industries.
Ultrasonic welding is a process that uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to join materials, typically thermoplastics or metals. The process involves applying pressure and ultrasonic energy to the materials, which generates heat through friction at the interface, melting the surfaces and creating a solid-state bond. It's commonly used in various industries, including automotive, medical devices, and electronics, due to its speed, efficiency, and ability to produce strong, clean joints without the need for adhesives or additional fasteners.
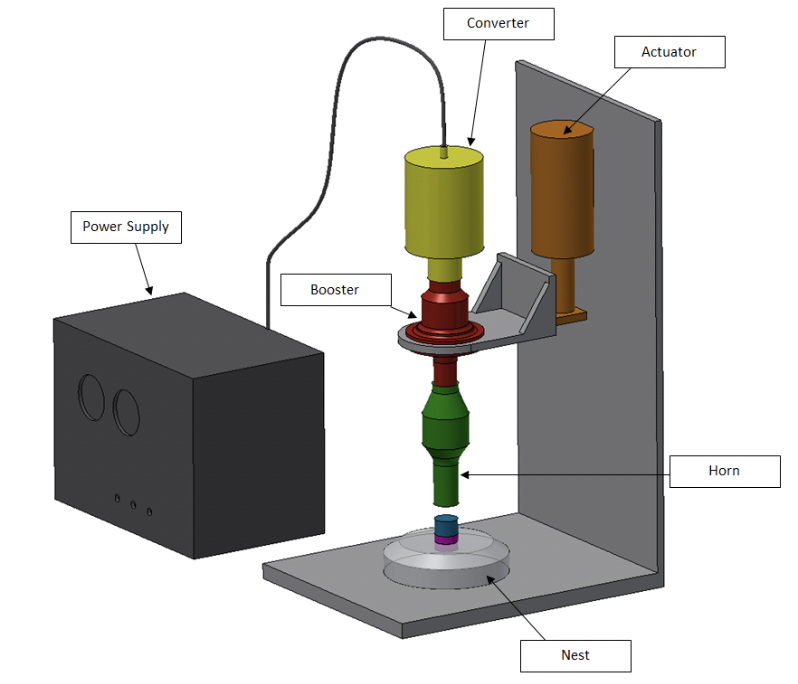
Ultrasonic welding is particularly effective for joining the following materials:
1. Thermoplastics: Commonly used plastics include:
o Polypropylene (PP)
o Polyethylene (PE)
o Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
o Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
o Nylon (PA)
o Polystyrene (PS)
2. Metals: Ultrasonic welding can also join certain metals, including:
o Aluminum
o Copper
o Nickel
o Gold
o Silver
3. Composites: Some composite materials that include thermoplastics can also be welded using this method.
4. Dissimilar Materials: Ultrasonic welding can sometimes join different materials, like plastics to metals, depending on their properties and the specific application.
The effectiveness of ultrasonic welding depends on factors like the material's thickness, shape, and acoustic properties.
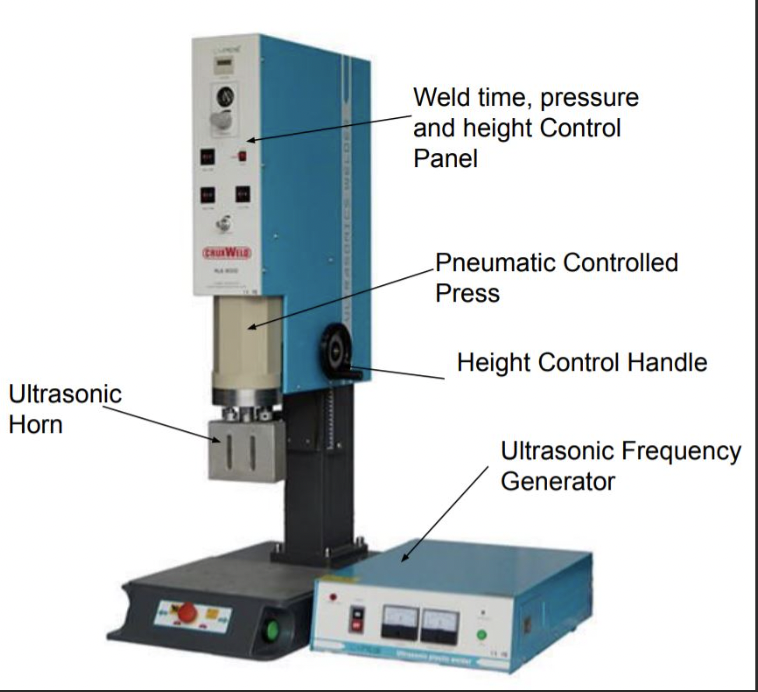

Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding:
1. Speed: The process is rapid, typically taking seconds to complete.
2. Strong Joints: It creates robust, durable bonds without the need for adhesives or fasteners.
3. Clean Process: There are no residues or contaminants, making it suitable for cleanroom environments.
4. Energy Efficiency: The process consumes less energy compared to other welding methods.
5. Automation: Easily integrated into automated production lines.
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding:
1. Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for ultrasonic welding; it works best with specific thermoplastics and metals.
2. Thickness Constraints: The thickness of materials can limit the effectiveness of the weld.
3. Initial Costs: Equipment can be expensive, which may be a barrier for small-scale applications.
4. Joint Design Requirements: Joints need specific designs to ensure effective energy transfer and bonding.
5. Potential for Damage: If not properly controlled, the process can damage delicate components.
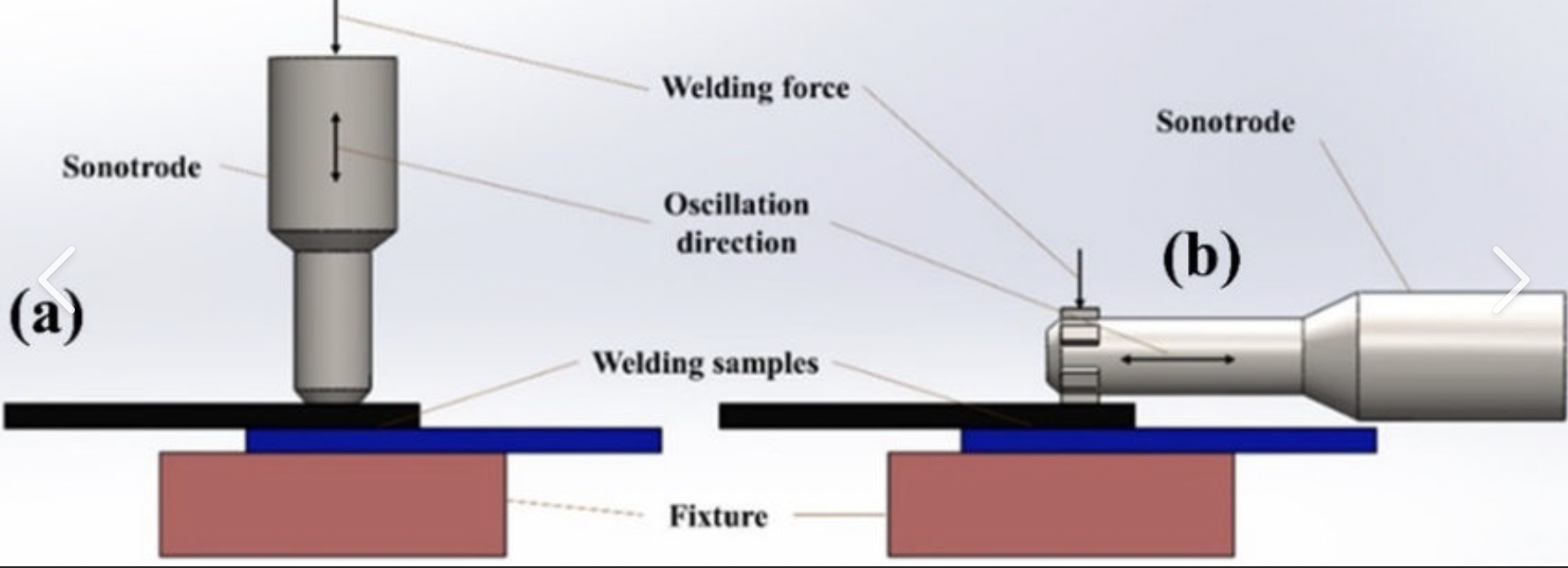
Ultrasonic welding is widely used in several industries, including:
1. Automotive: For joining plastic components, such as dashboards, door panels, and electrical connectors.
2. Medical Devices: In the production of medical equipment, including syringes, IV bags, and other disposable items, where cleanliness and strong seals are essential.
3. Electronics: Used for bonding components in devices like mobile phones, computers, and appliances, particularly in joining wires and connectors.
4. Packaging: Employed in sealing packaging materials, such as blister packs and flexible films, ensuring airtight seals.
5. Textiles: For bonding fabrics and non-woven materials in products like clothing, filters, and hygiene products.
6. Consumer Goods: Used in manufacturing various items, from toys to household appliances, where quick and strong joins are required.
7. Aerospace: Occasionally used for lightweight components and assemblies where strong, lightweight joints are critical.
These industries benefit from the speed, efficiency, and reliability of ultrasonic welding, making it a popular choice for many applications.
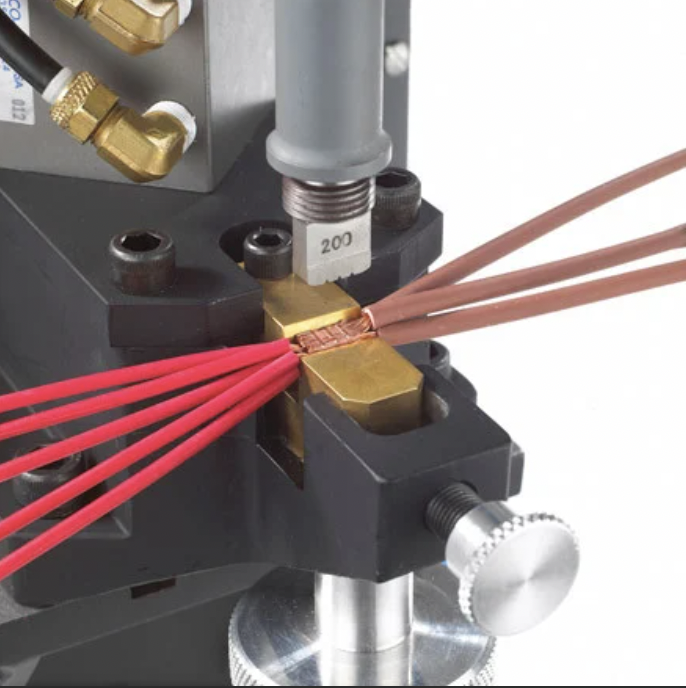
Differences Between Ultrasonic Welding and Traditional Welding:
1. Process Type:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to generate heat through friction, joining materials without melting them completely.
o Traditional Welding: Involves melting the base materials and often a filler material, allowing them to fuse as they cool.
2. Materials:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Primarily used for thermoplastics and certain metals.
o Traditional Welding: Suitable for a broader range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and more.
3. Heat Generation:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Generates localized heat at the joint interface without affecting the entire workpiece, reducing distortion.
o Traditional Welding: Heats the entire weld area, which can lead to warping or structural changes in surrounding materials.
4. Speed:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Typically much faster, often taking only a few seconds per weld.
o Traditional Welding: Can take longer due to the need for heating and cooling cycles.
5. Joint Cleanliness:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Produces clean, strong joints without residues, making it suitable for applications in clean environments.
o Traditional Welding: May require additional cleaning steps to remove slag, spatter, or other contaminants.
6. Equipment Cost:
o Ultrasonic Welding: Initial equipment costs can be high, but the process is generally more energy-efficient.
o Traditional Welding: Equipment can vary widely in cost, but traditional methods may require more extensive setups and maintenance.
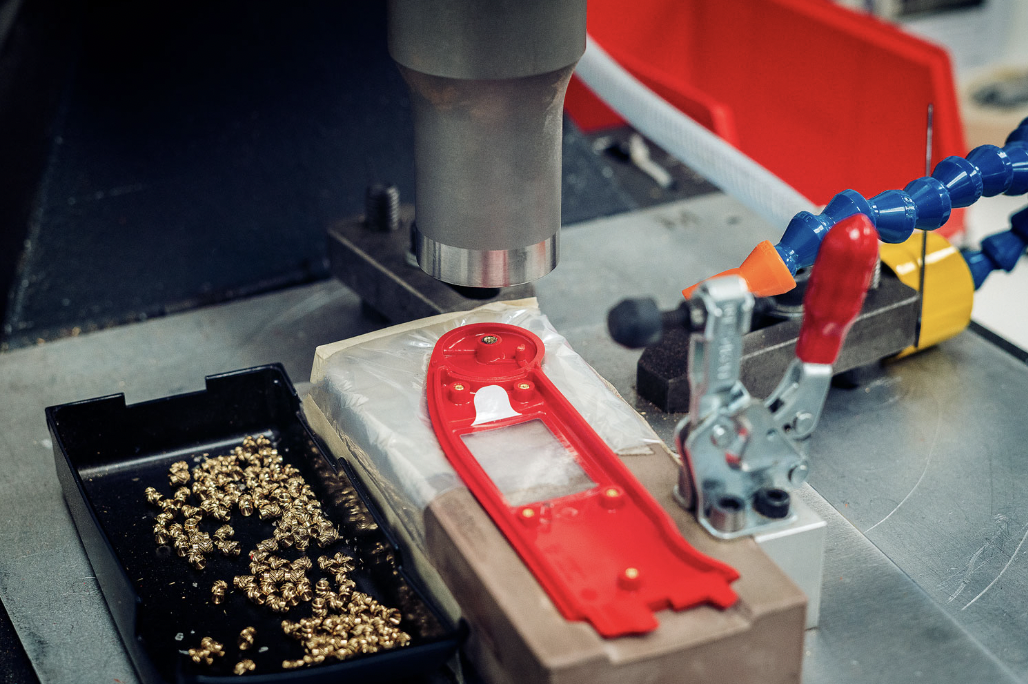

As the manufacturing sector continues to evolve, ultrasonic welding is proving to be an indispensable tool for achieving high-quality, efficient, and environmentally friendly production processes. Its ability to bond a variety of materials quickly and cleanly positions it as a frontrunner in modern welding technology.
By adopting ultrasonic welding, companies not only enhance their operational efficiency but also set a new standard for precision and sustainability in their manufacturing practices.
As we look to the future, the continued advancement of this technology promises to further reshape industries, paving the way for innovations that meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
Factory add: No 39, Zhen an west road, Changan town , Dong guan city, China.